Crypto Tax in India: Cryptocurrency, once viewed as a niche financial asset, has now become mainstream, attracting investors worldwide. However, with growing adoption comes tighter regulations, especially concerning crypto taxation. The Indian government has taken a particularly aggressive stance on crypto tax compliance, introducing stringent rules and heavy penalties.
In this article, we focus on “Crypto Tax in India” as the primary theme, with comparative insights into “Crypto Tax in the US” and other countries. We’ll discuss new Indian regulations, penalties, and global tax rates, followed by an extensive FAQ section.
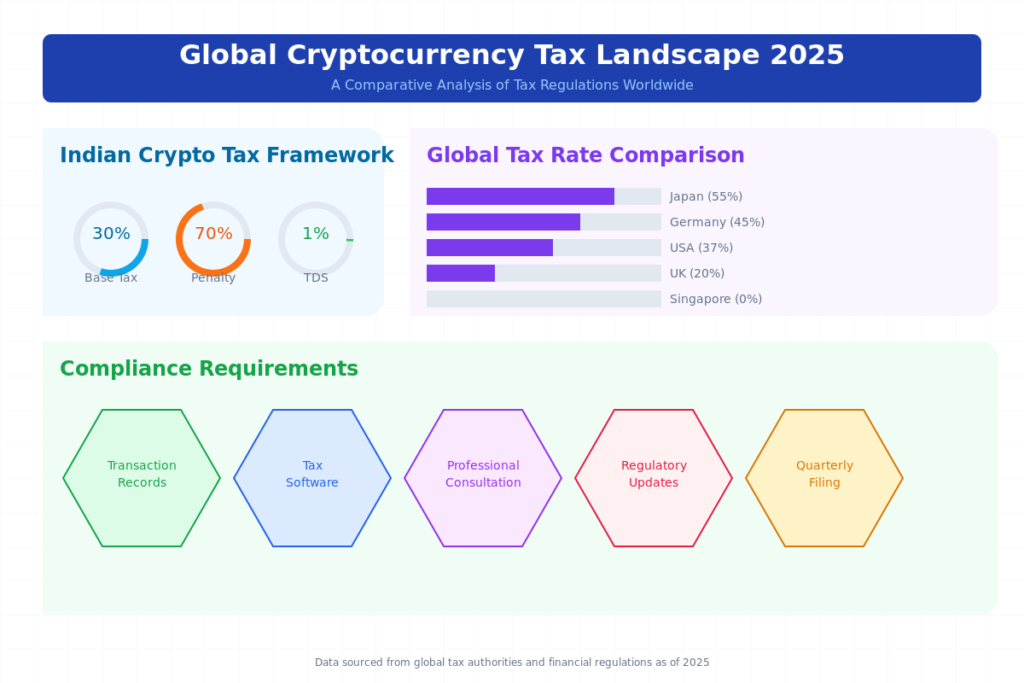
Crypto Tax in India: 70% Penalty for Unreported Gains
India has recently intensified its stance on crypto taxation. Under the Union Budget 2025, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman introduced amendments to Section 158B of the Income Tax Act:
Key Highlights:
- Flat 30% Tax: Profits from Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) are taxed at a flat 30% rate.
- 1% TDS (Tax Deducted at Source): Deducted on every crypto transaction.
- 70% Penalty for Unreported Gains: Failure to disclose crypto earnings may result in a penalty of up to 70%, applicable retroactively for the past four years.
- Mandatory Reporting: Crypto exchanges and financial institutions must report all crypto transactions to tax authorities.
Impact on Crypto Investors:
- Increased Compliance Costs: Traders must maintain meticulous records of transactions.
- Scrutiny of Global Exchanges: Platforms like Binance and Bybit have faced regulatory hurdles, with Bybit ceasing operations in India.
- GST on Crypto: Authorities uncovered $97 million in unpaid GST from crypto platforms, highlighting the government’s aggressive enforcement.
Crypto Tax in the US: Stricter Reporting from 2025
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has announced stricter crypto reporting requirements starting in 2025:
Key Changes:
- Mandatory Reporting: All digital asset transactions must be reported, regardless of value.
- 1099-DA Forms: Exchanges must issue 1099-DA forms to users, detailing their crypto earnings.
- Capital Gains Tax: Ranges from 0% to 37% based on income and holding period.
Penalties:
- Failure-to-Report Penalties: Can result in fines up to $25,000 and potential criminal charges.
- Legal Challenges: Some crypto advocacy groups are suing the IRS, claiming constitutional violations.
Crypto Tax Rates in Developed and Developing Countries
| Country | Tax Rate on Crypto Gains | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|
| India | 30% + 1% TDS + 70% penalty (if unreported) | Strict penalties for non-compliance |
| United States | 0% – 37% (Capital Gains Tax) | Mandatory reporting from 2025 |
| United Kingdom | 10% – 20% (Capital Gains Tax) | Exemptions for gains under £12,300 |
| Germany | 0% (if held >1 year), else up to 45% | Long-term holdings tax-free |
| Australia | 0% – 45% (Capital Gains Tax) | Depends on holding period |
| Canada | 50% of gains taxed as income | Business activities taxed at corporate rates |
| Singapore | 0% (no capital gains tax) | Crypto businesses taxed as regular income |
| Portugal | 28% (new rule from 2023) | Previously tax-free for individuals |
| South Korea | 20% on gains over 2.5 million KRW | Delayed implementation to 2025 |
| Japan | Up to 55% (progressive tax rate) | Classified as miscellaneous income |
| UAE (Dubai) | 0% (no personal income tax) | Crypto-friendly hub |
| Brazil | 15% – 22.5% (Capital Gains Tax) | Strict reporting for gains above $35,000/month |
| Russia | 13% – 15% (Personal Income Tax) | Proposed stricter regulations in 2025 |
| Nigeria | 10% (Capital Gains Tax) | New tax regime introduced in 2022 |
| South Africa | 18% (Capital Gains Tax) | Crypto classified as financial assets |
Why India Is Tightening Crypto Tax Laws
- Preventing Tax Evasion: Anonymity in crypto transactions makes them attractive for evasion.
- Increasing Revenue: As crypto markets grow, the government sees taxation as a significant revenue source.
- Regulatory Oversight: Controlling illicit activities like money laundering and terror financing.
- Investor Protection: Clear tax policies encourage responsible investing.
Challenges Faced by Indian Crypto Investors
- Complex Reporting: Difficulty in tracking multiple transactions across platforms.
- Ambiguous Guidelines: Frequent changes in regulations create confusion.
- Volatility Risks: Tax liabilities may arise even if crypto values fall after gains are realized.
Best Practices for Crypto Tax Compliance in India
- Maintain Detailed Records: Track every buy, sell, swap, and transfer.
- Use Crypto Tax Software: Platforms like Koinly, Zerion, and ClearTax simplify reporting.
- Consult Tax Professionals: Seek expert advice, especially for large portfolios.
- Stay Updated: Tax laws change rapidly; regular monitoring is crucial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Crypto Tax in India
1. What is crypto tax in India?
Crypto tax refers to the 30% flat tax on profits from Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs), with 1% TDS on transactions.
2. Is there a penalty for not reporting crypto gains?
Yes, up to 70% penalty for unreported gains, applicable retroactively for four years.
3. How do I report crypto income in India?
Through your Income Tax Return (ITR) under the Virtual Digital Assets section.
4. Are crypto-to-crypto trades taxable?
Yes, each trade is considered a taxable event.
5. Can I offset crypto losses against gains?
No, current Indian tax laws do not allow offsetting crypto losses.
6. Is there GST on crypto transactions?
Yes, applicable for crypto exchange platforms and large transactions.
7. What if I use crypto for purchases?
It’s treated as a disposal, triggering capital gains tax.
8. Are foreign crypto exchanges subject to Indian tax laws?
Yes, Indian residents must report all global crypto income.
9. How does India compare globally on crypto tax?
India’s tax regime is among the strictest, with high penalties and mandatory reporting.
10. Can crypto holdings be declared under the Black Money Act?
Undisclosed foreign crypto assets may fall under the Black Money Act, leading to severe penalties.
Conclusion
Crypto taxation in India has become stringent, with a 30% tax, 1% TDS, and penalties up to 70% for unreported gains. The government’s aggressive approach aims to regulate the booming crypto market, prevent tax evasion, and ensure financial transparency.
For Indian crypto investors, staying compliant, maintaining accurate records, and seeking professional advice are essential. As regulations evolve, awareness and proactive tax planning will be the key to navigating the complex landscape of crypto taxation in India.
You Might Also be Interested in: Union Budget 2025-26: Doubling Down on Employment Generation
Visual Summary of Crypto Tax in India