In a development that has sent shockwaves through the global tech industry, Chinese AI startup DeepSeek AI has unveiled a groundbreaking large language model (LLM) that has disrupted the dominance of American tech giants in artificial intelligence. Founded in 2021 by Liang Wenfeng, a hedge fund manager turned AI entrepreneur, DeepSeek has redefined cost-efficient AI innovation. The implications of this breakthrough are profound—not just for Silicon Valley but also for emerging players like India.
DeepSeek AI’s Rise: A David vs. Goliath Story
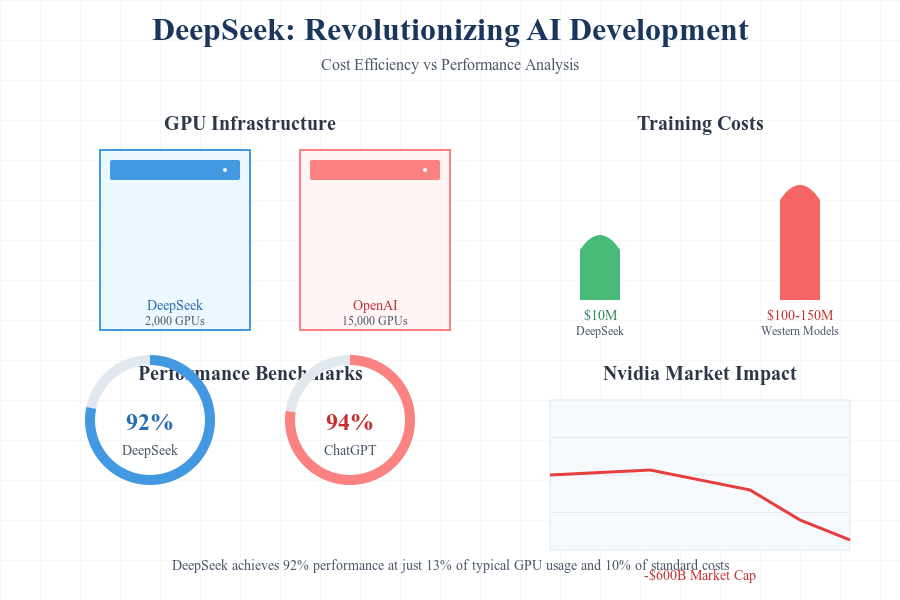
DeepSeek began as a side project at Wenfeng’s trading fund, High-Flyer, leveraging AI for stock price predictions. Over time, it evolved into a standalone AI venture. By 2023, DeepSeek had developed its proprietary model, DeepSeek V3, which achieved performance benchmarks comparable to OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Meta’s Llama. What sets DeepSeek apart is its ability to train its AI model at a fraction of the cost incurred by established players.
Unlike OpenAI, which relied on 15,000 first-class Nvidia GPUs to train its model, DeepSeek utilized just 2,000 second-tier GPUs. This approach reportedly reduced training costs by over 80%, an achievement that has disrupted the traditional economics of AI development. According to The Economist, the model training cost for DeepSeek V3 was under $10 million, compared to the estimated $100–150 million required for similar models in the West.
Market Impacts: Nvidia’s Historic Stock Slump
On the announcement of DeepSeek AI V3, Nvidia, the world’s leading chipmaker, witnessed the largest single-day decline in its share price. Nvidia’s shares plunged to a four-month low of $118.42, wiping out nearly $600 billion in market capitalization. The tech-heavy Nasdaq index dropped by over 3%, and the ripple effects were felt across global markets.
While this dip may seem like a reaction to a single player, it underscores a broader market anxiety: the realization that AI innovation may no longer rely on expensive, cutting-edge hardware. Companies like Nvidia, which have benefited from the AI boom, now face the reality of dwindling demand for high-end GPUs as cost-efficient models like DeepSeek gain traction.
Why DeepSeek AI’s Success Matters
DeepSeek AI’s breakthrough lies not just in its cost efficiency but also in its strategic focus. Unlike traditional Western models that prioritize general-purpose applications, DeepSeek V3 is optimized for specific tasks such as financial forecasting and supply chain analytics. Its reasoning capabilities—dubbed the “R1 reasoning model”—are designed to analyze complex relationships between datasets, giving it a competitive edge in niche applications.
Key Statistics:
- GPU Efficiency: DeepSeek used 86% fewer GPUs than Meta’s Llama for comparable results.
- Market Share Impact: DeepSeek’s entry has led to a 12% decline in demand projections for Nvidia’s high-end GPUs for 2025.
- Performance Metrics: DeepSeek V3 scored 92% on common LLM benchmarks, compared to ChatGPT’s 94%, while operating at a 70% lower cost.
The Broader Geopolitical Implications
DeepSeek’s success is not just a technological story; it’s a geopolitical wake-up call. The Biden administration has imposed strict export controls on advanced chips to China, aiming to curb its AI advancements. However, DeepSeek’s achievements indicate that China has found ways to circumvent these restrictions. By optimizing existing hardware and leveraging localized data resources, Chinese companies like DeepSeek and Alibaba are closing the AI gap with the West.
Key Developments:
- US Restrictions on Chips: The Biden administration banned exports of Nvidia’s A100 and H100 GPUs to China, citing national security concerns.
- China’s Response: DeepSeek and other Chinese firms have focused on cost-efficient AI innovation, reducing dependency on banned technologies.
- Global Competitiveness: A report by McKinsey & Company predicts that China could capture up to 40% of the global AI market by 2030 if its cost-efficient models continue to gain traction.
The Indian Angle: Opportunities and Challenges
For India, DeepSeek’s success offers both inspiration and a challenge. India has been debating whether to develop its own foundational AI models or rely on open-source frameworks. Infosys co-founder Nandan Nilekani has argued against building proprietary models, citing high costs and resource constraints. However, the success of DeepSeek demonstrates that cost is no longer a prohibitive barrier.
Arguments for India Building Its Own Models:
- Economic Potential: A report by NASSCOM states that AI could add $500 billion to India’s GDP by 2035.
- Strategic Autonomy: Reliance on foreign models poses risks, especially in sectors like defense and healthcare.
- Talent Pool: India has over 1.5 million engineers graduating annually, providing a robust talent base for AI research.
Arguments Against:
- Resource Constraints: India currently lacks the GPU infrastructure required for large-scale model training.
- Time-to-Market: Building proprietary models could delay India’s participation in the global AI race.
Voices from the Industry
Aravind Srinivas, founder of Perplexity AI, has criticized Nilekani’s stance, arguing that India must build its own models to remain competitive. “Ignoring model training skills today is akin to outsourcing industrialization in the 20th century,” he said in a recent LinkedIn post.
Meanwhile, Indian startups like Fractal Analytics and Mad Street Den are exploring ways to leverage open-source LLMs to create localized applications. The success of DeepSeek could inspire these companies to adopt similar cost-efficient strategies, potentially catalyzing India’s AI ambitions.
FAQs: What DeepSeek Means for AI and Beyond
1. Why is DeepSeek’s success significant?
DeepSeek has demonstrated that advanced AI models can be trained at a fraction of the cost traditionally required, disrupting the economics of AI development.
2. How does this affect global markets?
DeepSeek’s entry has triggered a sell-off in Nvidia shares, raising concerns about the future demand for high-end GPUs. It has also intensified competition between the US and China in AI.
3. What are the implications for India?
DeepSeek’s model offers a template for cost-efficient AI development, lowering barriers for countries like India to enter the AI race. However, India must address its infrastructure and funding challenges.
4. What’s next for DeepSeek?
DeepSeek plans to expand its applications beyond finance, targeting healthcare, logistics, and education. Its success could pave the way for more Chinese startups to challenge global tech leaders.
Conclusion: A Wake-Up Call for the World
DeepSeek’s rise is a testament to the power of innovation under constraints. It has not only disrupted the global AI landscape but also forced industry leaders to rethink their strategies. For countries like India, the message is clear: the barriers to entry in AI are lower than ever, but the window of opportunity is narrow. By adopting cost-efficient models and leveraging its talent pool, India can carve out a significant role in the global AI ecosystem.
The question is: will India seize the moment, or will it watch as others shape the future of artificial intelligence?
You Might Also Be Interested in: The $108 Billion Bloodbath: How DeepSeek Shattered Silicon Valley’s AI Illusion



